What is the Safety Data Sheet (SDS)?
A Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is an official and technical document containing health, safety, environmental and usage information about a chemical substance. This form is intended in particular for the purpose of preventing hazards that may occur during the production, storage, transportation or use of chemical substances
it is prepared. This document, which plays a vital role in terms of occupational health and safety, helps employers and employees to take the necessary measures by evaluating the risks.
It contains a lot of information in a systematic way, such as potential hazards of chemicals used in the workplace, appropriate protection measures, what to do in case of exposure, and disposal methods. Thus, both the health of employees is protected and environmental risks are minimized.
Who Can Prepare the Safety Data Sheet?
Safety Data Sheets can only be prepared by specialists who are authorized in this regard, have received the necessary training and have a certificate. These specialists are usually chemical engineers, environmental engineers, or occupational health and safety specialists. It is not appropriate for this form to be prepared by unauthorized persons due to the need for technical information and legal responsibilities in preparing it.
In addition, Safety Data Sheets should be updated periodically and prepared in accordance with the applicable legislation. Proper operation of this process ensures that the employer and employees are also protected from a legal point of view. The forms must also be followed by supervisory authorities (for example, the Ministry of Labor and Social Security, the Ministry of Environment, Urbanism and Climate Change).
What is the Purpose of the Safety Data Sheet?
The main purpose of the Safety Data Sheets; health and safety that may occur when working with chemical substances
it is to minimize safety hazards, ensure the safe use of these substances and prevent environmental damage.
Its main objectives are:
- To inform and protect employees against health problems that may be caused by chemical substances.
- To contribute to the prevention of occupational accidents and occupational diseases.
- To determine the standards for the safe storage, transportation and disposal of substances.
- To provide the necessary first aid and intervention methods for emergency situations.
- To ensure that environmental impacts are controlled.
In the light of this information, the employer can take the necessary measures both to ensure the safety of the workplace and to protect the health of the employee in a more conscious way.

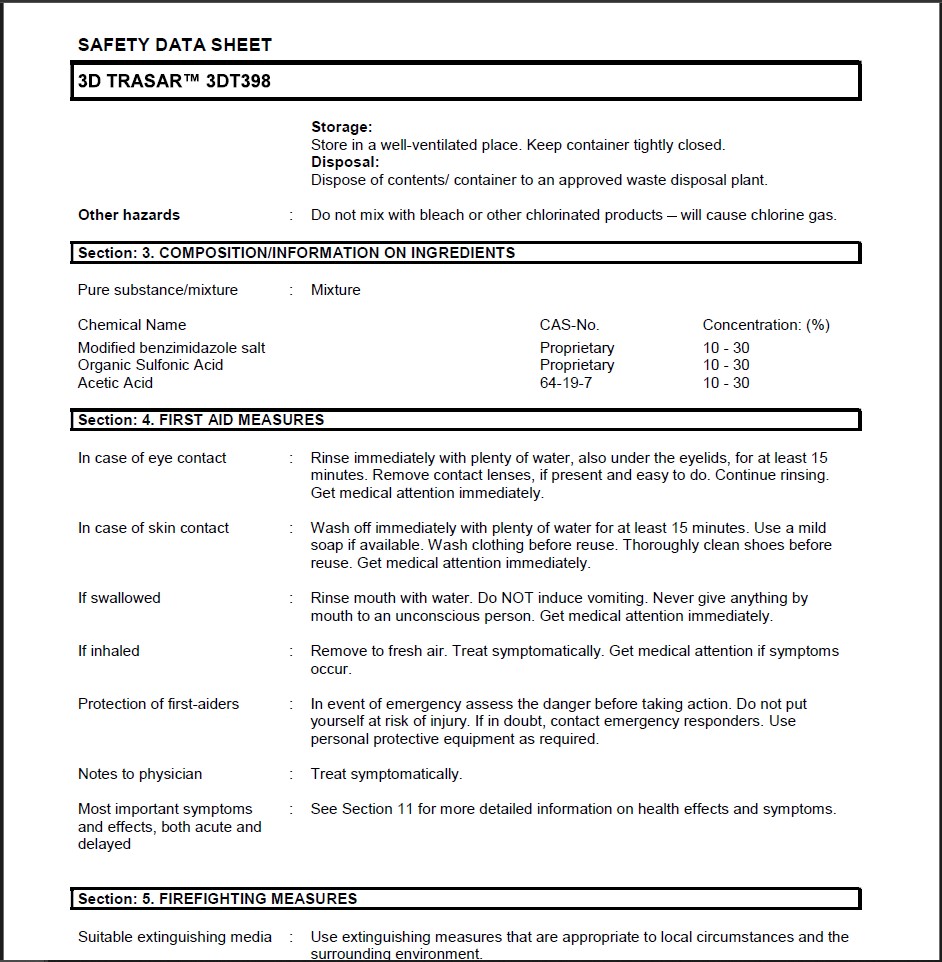
What Information Does the Safety Data Sheet Contain?
A Safety Data Sheet usually consists of detailed information sections collected under 16 main headings. These titles are:
- Substance/Preparation and Company Information
- Information about its Composition and Content
- Introduction of Dangers
- First Aid Measures
- Fire Fighting Measures
- Precautions Against Accidental Spread
- Handling and Storage
- Exposure Controls / Personal Protection
- Physical and Chemical Properties
- Stability and Reactivity
- Toxicological Information
- Ecological Information
- Disposal Information
- Transportation Information
- Regulatory Information
- Other Information
Under these headings, all technical and practical information from the properties of the chemical to the risk of exposure, from transportation procedures to environmental effects are included.
| SDS Header / Sample Information For Methanol | |
| Physical Condition | Colorless, volatile liquid |
| Danger | Highly flammable, toxic |
| Protective Equipment | Gloves, protective glasses, breathing mask |
| First Aid | Fresh air, eye washing, medical intervention |
| Disposal | According to hazardous waste regulations |
Methods of Protection with Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
It is vital to use proper PPE when working with chemical substances. The following protective equipment indicates the main precautions that can be taken against chemicals:
- Respiratory Protection: Mask with organic vapor filter
- Eye Protection: Chemical splash resistant glasses
- Skin Protection: Nitrile gloves, chemical resistant apron
- General Protection: Working in ventilated areas, using a closed system
Steps to Follow in Case of Chemical Spill
Since chemical spills can pose a serious risk, the following steps should be taken carefully:
1- To Ensure Security and to Raise an Alarm
- Turn off all fire/electricity sources.
- Open the windows, turn on the ventilation.
- Notify the authorities, activate the necessary alarms.
2- Use of Personal Protective Equipment
- Wear a mask, glasses, apron, gloves and chemical-protected boots.
3- Getting the Spill Under Control
- Use absorbent material and plastic equipment for small spills.
- In case of large spills, install a barrier and transfer to appropriate containers.
- Do not contact with water (for example, for methanol).
4- Cleaning and Disposal
- Neutralization (e.g. sodium bicarbonate may be required.
- After cleaning, the area should be rinsed with plenty of water.
- All waste should be disposed of as hazardous waste.
5- Exposure and Health Control
- Remove dirty clothes, the skin should be washed.
- Use an eye shower, get fresh air.
- Call for medical help.
6- Reporting and Record Keeping
- Fill out the incident form, update the exposure records.
- Legal notification should be made to the necessary authorities.
Summary Flow Chart:
- Provide Security
- Use PPE
- Limit Spillage
- Clean and Dispose of
- Do a Health Check
- Report and Keep a Record
as a result
Safety Data Sheets are not just a document; they are an indispensable part of the occupational health and safety culture. Being aware of chemical risks and taking measures against these risks based on scientific and legal bases are mandatory both from the point of view of individual health and corporate responsibility.
Every individual who works with chemicals should read this form correctly, understand it and integrate its requirements into their business processes.
